After glancing at a few developments in Japan’s news, something has hit me – Japan’s interest in the English language seems to be on the decline! Let me give you some examples along with my own speculation as to why this is happening:
Japan’s Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications reports that Japan’s municipalities will accept 5,508 foreigners as teachers/token foreigners in the JET program. More interestingly, this year marks the 4th straight decline in the number brought in by the program after a peak in 2002 (see the announcement for a clearer chart):
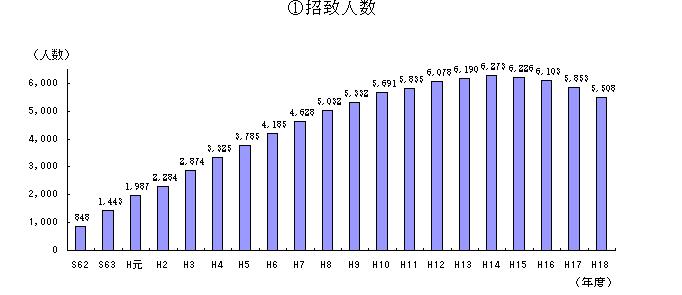
My explanation for this decline – JET salaries and other costs are covered by the central government in the form of kofuzei, or tax revenues collected from local governments and redistributed back so as to achieve an equilibrium in economic development nationwide. Since kofuzei has been the target of major cuts as part of Koizumi’s reform program to make outlying regions more autonomous, it’s likely that the municipalities had to make a decision between an ALT and money for a new bridge. Not a sign of a lack of interest per se, but the dynamic of the incentives to accept these people is changing, forcing towns to reexamine their priorities.
The decline in the English teaching market is even more striking in the private sector. FujiSankei Business-i examines the glut in English teachers in Japan in a July 12 article. According to NOVA’s estimates, the market may have peaked in 2004. The increased competition among schools is exerting pressure toward innovation, improvement of service, and the closure of schools (NOVA, the king of eikaiwa schools, is restructuring – not a good sign!). While this could spell a period of decline for the eikaiwa schools, maybe this will actually inspire the schools to actually get results.
The JET Program and private eikaiwa schools share the same essential method and selling point – put a recent college graduate from an English-speaking country in the room with Japanese person/people, wait for magic to happen. Call it English by Osmosis. For a long time college students have considered “teaching English in Japan” a valid first job option if nothing else panned out or if they really really liked Evangelion. But considering the above developments it could be only a matter of time before teaching English in Japan ceases to be an automatic option for undergrad students in English-speaking countries looking for something easy.
After something like 25 years of the “eikaiwa boom” it should come as no surprise that just about every Japanese person has given eikaiwa a try in one form or another. And once the majority realize that it’s not a magic replacement for a lack of motivation/talent, they get bored, leaving three things behind: 1) new generations of suckers; 2) hardcore students who know how to work the system and learn despite the flaws; and 3) disgruntled students who may no longer believe in the method. I realize that there are many teachers in Japan working very hard every day (I used to be one of them), but it is simply a flawed system.
And in a not unrelated development Japan’s pop culture is starting to look more into the Asian market these days at the expense of Hollywood. Just as we here in the US finally picked up on the trend of US celebrities making extra cash by appearing in Japanese commercials, it looks as though Hollywoord stars are no longer the commercial pull that they once were:
A Hollywood in-house secret, Japanese TV commercials were once talked about with a wink and a shake of the head. Piles of cash were paid to stars willing to peddle anything from whiskey to cigarettes, cars to coffee, instant noodles to cafe latte — as long as nobody told the fans back home. Hey, did you know Dennis Hopper did one for bath products? How much do you figure Leonardo DiCaprio got for that SUV spot? A million? Three?
Sadly, the days of seeing, say, Harrison Ford guzzling Kirin beer may be over. American stars have not vanished from the Japanese advertising landscape, but their numbers have dropped dramatically since the heyday of the 1990s, when even Mickey Rourke was considered bankable here.
The article goes on to say that the recent popularity of Korean dramas has spurred the shift in focus. Thankfully, the good times aren’t over – you can still see the many many ads that the Japan-pandering era produced at the wonderful Japander.com.
Another development in the background of all this is the political backlash against Koizumi’s reform agenda. Those who decry economic reform often cite their distaste for “market fundamentalism” (such as privatization of public corporations etc), considered a mechanical application of the American system to Japanese society. Regrdless of the validity of such claims (even though the US is unlikely to privatize its postal service anytime soon!), it may be inevitable that the anti-America rhetoric translates into fewer people taking up English as a hobby.
While the JET Program and eikaiwa schools are here to stay as an institution in Japan, it seems to me that the underlying support for grassroots English interest is waning a bit – the Japanese are getting a little bored with the “English through osmosis” model. While I dread the uncomfortable oyaji conversations that will no doubt result from the popularity of tripe like Dignity of a Nation, Japan’s shift away from its fascination with English/Hollywood (and perhaps by extension the rest of Europe/the entire “white race”) may at least have the fortunate side effect of making people realize that foreign-born TV personalities in Japan such as Dave Spector and Pakkun aren’t intrinsically all that interesting despite their mad Japanese skills. One can only hope.
But seriously, getting away from this flawed approach toward language learning is a promising sign for Japan. I tend to agree with calls to “learn Japanese first” (made in a recently popular anti-American diatribe Dignity of a Nation and elsewhere) that recently seem to be hitting a nerve. The logic in Japan of “English is the world language, so everyone needs to study English” is just basically wrong (as is the general curriculum that forces students to memorize a series of codes that only happen to be English and have no bearing on applied use of the language). In short, if you don’t learn your native language well and can’t express yourself on a deep level, there’s not much point in you being conversant in another language – you’ll have nothing to say! I think it’s best to provide quality opportunities for people to learn languages, and encourage those who are interested to pursue it to a high level. That might not make Japan into a nation of English speakers, but I don’t think that it’s politically possible for Japan to take the real steps needed to do that (i.e. make English essentially a second official language).
And another thing: it’s a little unfair for the JET Program to lure some 5k foreigners to Japan every year knowing that most of them are wasting their time. Considering that everyone is hired on contracts that last a maximum of 3 years, just what do 2 years at an elementary school or sitting at a desk in a city hall in the middle of nowhere in Japan have to offer anyone in terms of skills that can be applied elsewhere (outside maybe education)? In my own experience, I have met dozens of former JETs who are completely at a loss for what to do after completing terms in JET. They often want to use their Japanese language skills in their careers but for a number of reasons (never got any decent chance to take their Japanese to a high level, no meaningful job training except very little in education, and no meaningful further job opportunities for them inside Japan) it just doesn’t happen. But at the same time I can understand the mass interest in Japan and the eagerness of college grads to take a job in an interesting foreign country.
But rather than frittering their time away in a classroom, both sides would be better served if Japan had a JET Program for areas in which the country actually needs foreigners, like nursing, factories, finance, and IT jobs. Some recent proposals to promote these less parasitic foreigners, such as enhancement of visa programs, elimination of corrupt “language schools” and “entertainment visas” that serve as hotbeds of illegal immigration and crime, and attraction of more foreign students, whose numbers keep growing, are intriguing steps in the right direction IMO. This way, maybe all those people thinking about living in Japan might try studying something in a field that they know Japan needs, so when it comes time to graduate maybe they can get jobs that actually contribute to Japan’s GDP rather than padding its massive fiscal deficit. And for the Japanese, perhaps living in tandem with folks like this will provide a real incentive (“This person is my neighbor and I want to be her friend” rather than “I don’t want to waste the lessons I’ve already paid for”) to deal with foreigners and perhaps actually acquire the diversity and fresh experience that they seem so willing to pay for with eikaiwa.


